The Compact-Flash Wildcard and
CF Card Software Package User Guide
<< Previous | Next>>
Hardware
Overview
The CF Wildcard comprises a Wildcard bus header, digital interface chips, module address selection jumpers, and a CF Card Socket. The CF Card Software transparently controls the hardware interface to the CF Card.
The CF Wildcard supports standard ATA-compatible Compact Flash cards. These are available in sizes up to hundreds of Megabytes. Sandisk is reportedly the largest manufacturer of these cards, and the hardware and software have been fully tested using their SDCFB Compact Flash cards. We also recommend the Compact Flash PC Card Adapter which makes it easy to exchange data files from a laptop PC to and from the Mosaic Controller via the CF Wildcard. CF cards and adapters can be purchased from Mosaic Industries or computer store retailers.
To connect the CF Wildcard to the Wildcard Bus on the controller board, follow these simple steps:
With the power off, connect the female 24-pin side of the stacking go-through Wildcard bus header on the bottom of the CF Wildcard to Wildcard Port 0 or Wildcard Port 1 on the controller or its mating PowerDock. The corner mounting holes on the Wildcard should line up with the standoffs on the controller board. The Wildcard ports are labeled on the silkscreen of the controller board. Note that the CF Wildcard headers are configured to allow direct stacking onto the controller board, even if other Wildcards are also installed. Do not use ribbon cables to connect the CF Wildcard to the Wildcard bus. Use of ribbon cables on the UART Wildcard’s field header is fine.
CAUTION: The Wildcard bus on the controller board does not have keyed connectors. Be sure to insert the Wildcard so that all pins are connected. The Wildcard bus and the CF Wildcard can be permanently damaged if the connection is done incorrectly.
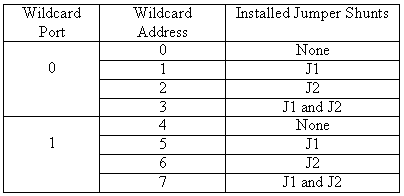
Once you have connected the CF Wildcard to the Mosaic controller, you must set the address of the wildcard using jumper shunts across J1 and J2.
The Wildcard Select Jumpers, labeled J1 and J2, select a 2-bit code that sets a unique address on the wildcard port of the Mosaic controller. Each wildcard port on the Mosaic controller accommodates up to 4 wildcards. Wildcard Port 0 on the Mosaic controller provides access to wildcards 0-3 while Wildcard Port 1 provides access to wildcards 4-7. Two wildcards on the same port cannot have the same address (jumper settings). Table 1 shows the possible jumper settings and the corresponding addresses.
Table 1: Jumper Settings and Associated Addresses
Install a Compact Flash Card into the socket on the CF Wildcard. These cards are designed to fit into the sockets only one way. Damage may occur to the CF card or the socket if the card is forced into the socket in an incorrect orientation.
Once the hardware and software are properly configured, files on the CF Card can be created, read, written, and manipulated by the pre-coded high-level driver routines. You can run the file system demonstration program as described in the readme.txt file on the File System distribution diskette, or read the comments of the FILEDEMO code listing in this document.
<< Previous | Next>>
| 




